[FSG] Faculty é of Sciences G é nies & Environment Department
1.- TYPICAL PATH
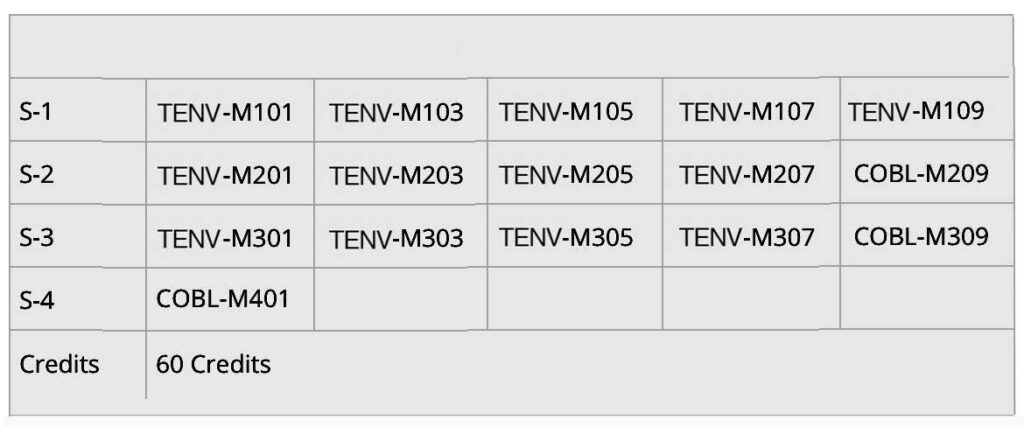
This program offers a typical full-time path spanning 2 years (4 sessions). Students wishing to continue their studies part-time are invited to contact the Faculty’s resource person. The program totals 60 credits, including 15 credits for the technical research project.
|
MASTER OF ENGINEERING ENVIRONMENT / TECH. ENVIRONMENTAL / 60 credits
Compulsory courses |
- COBL-M209 Technical Writing Methodology (3)
- COBL-M309 Research Quote / Dissertation (3)
- COBL-M401 Defense / Thesis (15)
2. OBJECTIVES
Train specialists in the development of clean technologies, processes, methods or tools that support these technologies, in order to solve environmental problems attributable to human activities. To do this, the student acquires in this program advanced knowledge in the field of environmental engineering, including scientific and technical knowledge relating to ecosystems, analytical techniques and treatment or remediation techniques.
The student will also acquire the skills and aptitudes necessary to analyze the technical, economic, social and environmental issues of a complex problematic situation, to design preventive, corrective or curative solutions, and to validate the conformity of a solution and its implementation according to the requirements of industries, municipalities or government institutions and the socio-economic and environmental issues of its long-term use.
3.- COURSE DESCRIPTION
This course is a systematic overview of the problem of sustainable development in a world where the use of exhaustible resources is necessary, in particular environmental resources. The analysis of this problem is made according to two inseparable paths, one qualified as positive and the other as normative, in the sense that it proposes interventions of a politico-economic nature.
Classification of hydraulic structures: water supply, hydroelectricity, flood control, navigation, drainage and sanitation. Acquisition of topographic, geological and geotechnical data. Hydrological studies. Design and sizing: water intakes, canals and pipes, spillways, energy dissipators, restitution structures. Transient phenomena and equilibrium chambers. Modeling and numerical simulation of flow conditions in hydraulic passages. Financial, environmental and socio-economic impacts. Pre-project of a hydroelectric development: choice, location and sizing of structures.
The data. Their shaping. Probabilistic models. Applications of probabilistic models to observed facts. Notions of errors. Adjustment of a function. Stochastic bonds: correlation and autocorrelation. Principal component analysis. Linear transfer functions.
This course aims to allow the student to acquire the knowledge, principles and techniques suitable for approaching the problems of water table management for the optimization of crop yields or other objective, to propose solutions able to solve them, plan and design underground drainage systems. Importance and history of irrigation. Irrigation needs. Types of irrigation systems. Design of irrigation systems. Determination of costs. Water supply. Quality of irrigation water. Pumping. Sprinkler irrigation systems. Hydraulic design of pipeline networks. Surface irrigation. Micro-irrigation. CROPWAT software.
Participants are made aware of the complexity and challenges of environmental management from case studies, real-life examples and more theoretical reflections. Environmental management systems, more particularly the ISO 14000 standards, serve as a backdrop for a more global analysis of the human and strategic aspects of the taking into account of sustainable development by organizations.
Hydrology & water purification (3 cr.)
The course covers wastewater treatment systems, in particular: preliminary and primary treatments as well as the activated sludge process (removal of carbon and nitrogen). At the end of this course, the student will be able to design all the elements of the wastewater collection networks. Hydraulic characteristics of flows in sewer lines. Urban runoff. Volumes and flows of sanitary wastewater. Sewage system design standards. Hydraulic design of sanitary and storm sewer networks.
Hydraulics & water purification (3 cr.)
At the end of this course, the student will be able to design all the elements of drinking water distribution networks. Hydraulic characteristics of flows in water distribution pipes. Consumption water volumes and flow rates. Collection, supply and distribution of drinking water. Design of a drinking water distribution network. Pipe auscultation techniques. Rehabilitation of aqueduct pipes. Laboratory sessions and practical work on the application of network design rules. Session projects on manual and computer design of wastewater distribution and collection networks.
Environmental geotechnics: retaining structures (earthen dikes) (design and construction), slope stability, environmental barriers, site characterization tools (piezocone, permeameter, resistivity cone) geomembranes, geotextiles, soil improvement (injection, trench of mud).
This course deals with research, its place in society as well as its achievement, researchers and communication, within the framework of research. It is divided as follows: scientific research and society; knowledge structure; organization of scientific research; carrying out the research; communication of research results; master’s and doctoral studies; ethics in research.
This seminar takes place before an assembly of professors, students and outsiders. During the seminar, the master’s student presents the main part of his research work and brings out the main conclusions. This presentation makes it possible to have discussions likely to orient and improve the student’s research.
This seminar takes place before an assembly of professors, students and outsiders. During the seminar, the master’s student presents the main part of his research work and brings out the main conclusions. This presentation makes it possible to have discussions likely to orient and improve the student’s research.
Reminder of the basics of hydraulics and hydrology. Introduction to hydrological and hydraulic modeling. Notions of statistical hydrology: frequency analysis, hydrological risk. Maximum precipitation likely. Net precipitation according to the SCS method. Synthetic unit hydrograph. Modified Puls Muskingum-Cunge rolling techniques. Climate change and water resources: climate models, scenarios, impacts on flows. Snow hydrology. Hydraulics and ice mechanics. Erosion in river. River construction methods. Learning formula by design project: The project will integrate several elements among the following: cofferdams, diversion canals, dikes, retaining structures, bridges. Projects including: Frequency analysis in hydrology, design of temporary and permanent hydraulic structures, flood zones, climate change and water resources, ice mechanics and hydraulics.
The student will have to write a preliminary report highlighting the following concepts. Water quality in the design and operation of drinking water distribution networks. Introduction to real-time control of unit networks. The pluvial network in double drainage.
The research activities carried out within the framework of a master’s program aim to prepare the writing of the dissertation, which aims to allow the student, through sustained contact with the practice of research or creation, to acquire the methodology appropriate to the exploration and synthesis of a field of knowledge and demonstrate knowledge of the writings and works relating to his subject of study.
COBL-M401. Master’s thesis defense (15 cr.)
Information
PROGRAMS
DEGREES
The bachelor’s degree in civil engineering will give you the tools that will allow you to meet the challenges of this field. Your training will allow you to assimilate the fundamental subjects of civil engineering, from the mechanics of deformable solids to the environment, including hydraulics, soil mechanics and project management. Bachelor of Civil Engineering (B. Ing.)
The civil engineer must sometimes specialize before tackling highly complex technical challenges. You will have the chance to study in a stimulating research environment including several laboratories in hydraulics, environment, geotechnics and structure and concrete.
The doctoral program will allow you to specialize in a field of civil engineering while acquiring specific training in research. Students have access to several laboratories with state-of-the-art facilities and equipment.
This bachelor’s degree will give you the tools you need to prevent pollution and alteration of the aquatic environment. The particularity of water engineering is its marked orientation towards integrated and sustainable water management.
Civil engineers today face the challenge of building and maintaining sustainable infrastructure. Water is one of the world’s essential resources. The objective of this study program assesses the evolution of water problems facing us and future generations.
Learn in this program about:
-
- Hydrology
- Water resources
- Management of infrastructure and public services
Be prepared to deal with infrastructure issues and evolving water issues. You will acquire the skills to take advantage of engineering concepts and computer technology to create a more sustainable infrastructure.
You will have the chance to study in a dynamic research environment comprising several laboratories in hydraulics, environment and geotechnics. You will meet students from various backgrounds and you will acquire knowledge in various disciplines relevant to environmental sciences. You will carry out teamwork and integration projects, which will open you up to interdisciplinary work in the environment.
This program will provide you with comprehensive training as a specialist in the design and operation of electrical and electronic systems. You will acquire the theoretical knowledge necessary for the study and design of technological systems as well as the experimental working methods required by the engineering profession.
The Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Engineering trains engineers and specialists in a wide variety of advanced technological fields. Thanks to the numerous research and development projects carried out in collaboration with industry and certain research centers, the training courses are well anchored in the reality of the environment.
You will perfect your skills in one of the fields of electrical engineering and you will contribute, through the results of your research, to the progress of science. The Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Engineering trains engineers and specialists in a wide variety of advanced technological fields.
This program will make you a specialist in hardware and software design of computer devices and systems. You will assimilate in particular the theoretical notions of signal and information processing as well as the architecture and organization of computer systems.
















 Département d’éducation physique d’éducation
Département d’éducation physique d’éducation Département des sciences végétales
Département des sciences végétales Département de science politique
Département de science politique  Département de psychiatrie
Département de psychiatrie Département de radiologie
Département de radiologie Département de Sociologie
Département de Sociologie
 Département de Génie des Sols et Agroalimentaire
Département de Génie des Sols et Agroalimentaire
 Département de chirurgie
Département de chirurgie Département de Sciences du bois et de la forêt
Département de Sciences du bois et de la forêt