FSG
Faculty Science and Engineering Tracking
[FSG] Faculty of Science and Engineering Tracking
Department of Civil Engineering
1.- COURSE
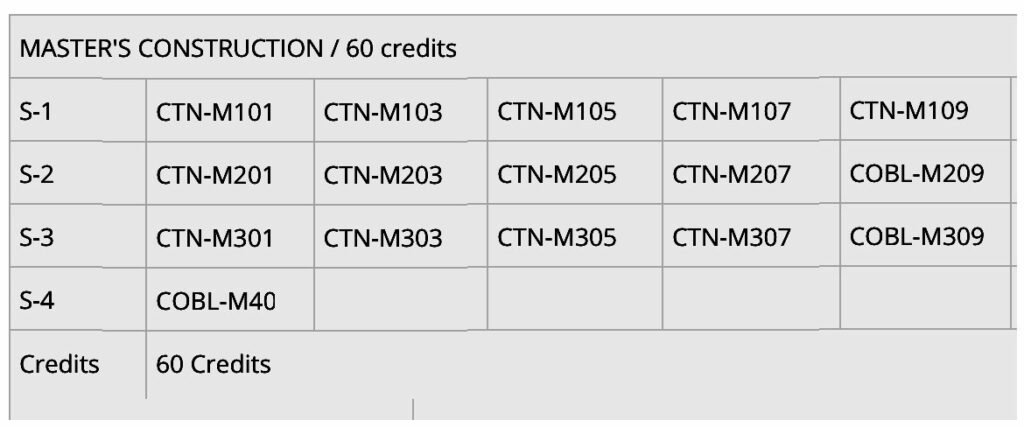
This program offers a typical full-time path spanning 2 years (4 sessions). Students wishing to continue their studies part-time are invited to contact the Faculty’s resource person. The program totals 60 credits, including 15 credits for the technical research project.
|
Compulsory courses |
- COBL-M209 Technical & scientific writing methodology (3)
- COBL-M309 Research Quote / Dissertation (3)
- COBL-M401 Defense / Thesis (15)
2. OBJECTIVES
Learn not only to design construction projects, but also to manage them. Increase its expertise in the design, process or management of construction and rehabilitation of building projects, road infrastructure, water infrastructure and resources, geotechnics and engineering structures. The profile with project offers the candidate the opportunity to deepen his knowledge to specialize in the chosen field, while learning about research. This specialized training allows you to better perform functions in the chosen field such as the direction or management of construction, maintenance and rehabilitation projects, their organization as well as the resolution of technical challenges related to the realization of projects. construction and rehabilitation.
You will therefore be called upon, throughout your training, to resolve concrete issues in the construction industry, including:
- the direction of construction works;
- project management, both in terms of their organization or improvement as well as the resolution of technical problems;
- research, innovation and design of construction works and civil infrastructure;
- the processes, methods and techniques for the design, implementation, evaluation, management, maintenance and rehabilitation of building, road infrastructure, hydraulics and hydrology, geotechnical, works of art, etc.
Following this course, the student will be able to:
- to size retaining walls;
- calculate the stresses in the soil under structures;
- to design simple superficial and deep foundations.
3.- COURSE DESCRIPTION
Retaining walls: thrust, stop, stability conditions, types of walls and construction methods. Sheet piles, diaphragm walls, armored excavations. Conventional foundations: footings and rafts. Piles: types of piles, capacity, installation methods, driving formulas, tests.
Definition of prestressing and its embodiments. General principles and prestressing. Material properties. Study on prestressing losses. Sizing of isostatic and hyperstatic beams: choice of the cross section, calculation of the required prestress, layout of the average cable. Mixed section beams. Instant and delayed deformations of prestressed parts. Prestressed reinforced concrete. Ultimate limit states of bending, shearing force and torsion.
At the end of this course, the student will be able to:
- explain the basic principles of structural steel design;
- to check the main elements of a steel frame:
- according to the calculation rules of the Canadian standard CAN / CSA S16;
- using tables from the Handbook of Steel Construction;
- using structural calculation software.
Steel and its properties, parts in tension, parts in pure compression, flexed parts, composite beams, assembled beams, overall stability of steel frames, column-beams, bolted and welded joints, calculation of the structure of buildings, fatigue. Basic principles, practical examples, use of computers.
Introduction to wood frames. Assessment of charges. Wood frame construction and structural forms. Technical properties of engineered wood used for structural elements. Calculation of bent elements, compressed and tensioned elements and elements subjected to combined loading. Calculation of assemblies. Calculation of lateral load resistance systems. Temporary wooden constructions. Applicable charges. Typical calculations and realizations of formwork and scaffolding.
Main materials treated: plastics, aggregates, cement concrete, bituminous mixes, rehabilitation materials and wood.
Introduction to the mechanics of continuous media: stress tensor, stress / strain relations, stress transformation and failure criteria. Fundamentals of elasticity theory and its typical applications. Energy methods: principle of virtual work, Maxwell-Betti and Castigliano theorems and resolution of hyperstatic systems. Theory of flexural plates. Hulls of revolution with axisymmetric loading. Axisymmetric thick-walled bodies, autofrettage and rotating discs. Theory of beams on elastic foundations and its applications to cylindrical shells. Stresses of thermal origin. Bending of curved beams and rings and applications to bolted flange joints. Advanced torsion: membrane analogy method (Prandtl),bars with thin open section and torsion of composite sections with limited warping section
The course covers wastewater treatment systems, in particular: preliminary and primary treatments as well as the activated sludge process (removal of carbon and nitrogen). At the end of this course, the student will be able to design all the elements of the wastewater collection networks. Hydraulic characteristics of flows in sewer lines. Urban runoff. Volumes and flows of sanitary wastewater. Sewage system design standards. Hydraulic design of sanitary and storm sewer networks.
At the end of this course, the student will be able to design all the elements of drinking water distribution networks.
Hydraulic characteristics of flows in water distribution pipes. Consumption water volumes and flow rates. Collection, supply and distribution of drinking water. Design of a drinking water distribution network. Pipe auscultation techniques. Rehabilitation of aqueduct pipes. Laboratory sessions and practical work on the application of network design rules. Session projects on manual and computer design of wastewater distribution and collection networks.
Environmental geotechnics: retaining structures (earthen dikes) (design and construction), slope stability, environmental barriers, site characterization tools (piezocone, permeameter, resistivity cone) geomembranes, geotextiles, soil improvement (injection, trench of mud).
Following this course, the student will be able to apply the basic principles of good project management taking into account all the dimensions of the urban environment. Principles of project management. Project planning. Integration of the technical constraints of the projects with the socio-economic and environmental aspects of the urban environment. Risk management. Maintenance of services during the construction phase. Case studies.
This course deals with research, its place in society as well as its achievement, researchers and communication, within the framework of research. It is divided as follows: scientific research and society; knowledge structure; organization of scientific research; carrying out the research; communication of research results; master’s and doctoral studies; ethics in research.
Activity intended for two categories of students:
- those who participate in the various engineering competitions;
- and those who wish to carry out research initiation work (development of a literature review, definition of a problem, or other).
In both cases, they must first have the director of the department approve a written proposal specifying the objective, the necessary means and the methodology they intend to use to carry out their project. This activity leads to the drafting of a technical report and an oral presentation.
Activity intended for two categories of students:
- those who participate in the various engineering competitions;
- and those who wish to carry out research initiation work (development of a literature review, definition of a problem, or other).
In both cases, they must first have the director of the department approve a written proposal specifying the objective, the necessary means and the methodology they intend to use to carry out their project. This activity leads to the drafting of a technical report and an oral presentation.
Activity intended for two categories of students:
- those who participate in the various engineering competitions;
- and those who wish to carry out research initiation work (development of a literature review, definition of a problem, or other).
In both cases, they must first have the director of the department approve a written proposal specifying the objective, the necessary means and the methodology they intend to use to carry out their project. This activity leads to the drafting of a technical report and an oral presentation.
Following this course, the student will be able to:
- evaluate and characterize the roads in terms of the network and the project plan by applying the concepts of precision and repeatability;
- to set up a road data bank;
- identify the laboratory and field tests required to confirm the cause of deterioration;
- to carry out economic analyzes according to the concept of the life cycle.
Maintenance policies and strategies. Maintenance techniques: routine maintenance, surface treatment, rehabilitation or recycling, resurfacing and reinforcement. Assessment methods. Databases. Economic analysis. Pavement maintenance management system: determination of required maintenance, choice of priorities, cost estimate, annual work schedule, determination of required resources. Quality control. Laboratory exercises and practical work on maintenance techniques for road networks.
The research activities carried out as part of a master’s program aim to prepare the writing of the dissertation, which aims to allow the student, through sustained contact with the practice of research or creation, to acquire the methodology appropriate to the exploration and synthesis of a field of knowledge and demonstrate knowledge of the writings and works relating to his subject of study.
COBL-M401. Thesis defense (15 cr.)
INFORMATION
PROGRAMS
DEGREES
The Bachelor of Civil Engineering will give you the tools that will allow you to meet the challenges of this field. Your training will allow you to assimilate the fundamental subjects of civil engineering, from the mechanics of deformable solids to the environment, including hydraulics, soil mechanics and project management. Bachelor of Civil Engineering (B. Ing.)
The civil engineer must sometimes specialize before tackling technical challenges of high complexity. You will have the chance to study in a stimulating research environment comprising several laboratories in hydraulics, environment, geotechnics and structure and concrete.
The doctoral program will allow you to specialize in a field of civil engineering while acquiring specific research training. Students have access to several laboratories equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and equipment.
This bachelor’s degree will give you the tools you need to prevent pollution and alteration of the water environment. The particularity of water engineering is its marked orientation towards integrated and sustainable water management.
Today’s civil engineers face the challenge of building and maintaining a sustainable infrastructures. One of the world’s critical resources is water. The focus of this degree program assesses the evolving water concerns facing us and future generations.
Learn in this program about:
-
- Hydrology
- Water resources
- Infrastructure and utility management
Be ready to tackle infrastructure-related issues and changing water concerns. You will gain the skills to leverage engineering concepts and computer technology to create a more sustainable infrastructure.
You will have the chance to study in a dynamic research environment comprising several laboratories in hydraulics, environment and geotechnics. You will rub shoulders with students with diverse backgrounds and you will acquire knowledge in various disciplines relevant to environmental sciences. You will carry out teamwork and integration projects, which will open you up to interdisciplinary work in the environment.
This program will provide you with comprehensive training as a specialist in the design and operation of electrical and electronic systems. You will acquire the theoretical knowledge necessary for the study and design of technological systems as well as the experimental working methods required by the engineering profession.
The Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Engineering trains engineers and specialists in a wide variety of advanced technological fields. Thanks to the numerous research and development projects carried out in collaboration with industry and certain research centers, the training courses are well anchored in the reality of the environment.
You will improve your skills in one of the fields of electrical engineering and you will contribute, through the results of your research, to the progress of science. The Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Engineering trains engineers and specialists in a wide variety of advanced technological fields.
This program will make you a specialist in hardware and software design of devices and computer systems. You will assimilate in particular the theoretical notions of signal and information processing as well as the architecture and organization of computer systems.
















 Département d’éducation physique d’éducation
Département d’éducation physique d’éducation Département des sciences végétales
Département des sciences végétales Département de science politique
Département de science politique  Département de psychiatrie
Département de psychiatrie Département de radiologie
Département de radiologie Département de Sociologie
Département de Sociologie
 Département de Génie des Sols et Agroalimentaire
Département de Génie des Sols et Agroalimentaire
 Département de chirurgie
Département de chirurgie Département de Sciences du bois et de la forêt
Département de Sciences du bois et de la forêt